
Mastering Negation: The Indispensable Role of Modals of Inability Worksheets
In the intricate tapestry of English grammar, expressing what we cannot do is just as crucial as expressing what we can. Modals of inability – primarily "can’t," "couldn’t," and "be unable to" – are fundamental linguistic tools that allow speakers and writers to convey limitations, restrictions, and failures to accomplish tasks or actions. For English language learners, mastering these nuanced expressions is a critical step towards achieving communicative competence and fluency. While theoretical explanations in textbooks lay the groundwork, it is through practical application and repeated exposure that true understanding solidifies. This is where well-designed modals of inability worksheets emerge as an invaluable, indeed indispensable, resource for both educators and students alike.
This comprehensive article will delve into the significance of modals of inability, explore the diverse types of exercises that can be incorporated into effective worksheets, discuss their pedagogical benefits, and provide insights into designing and utilizing them to their fullest potential.
Understanding Modals of Inability: The Core Concepts

Before diving into the utility of worksheets, let’s briefly revisit the core modals of inability:
-
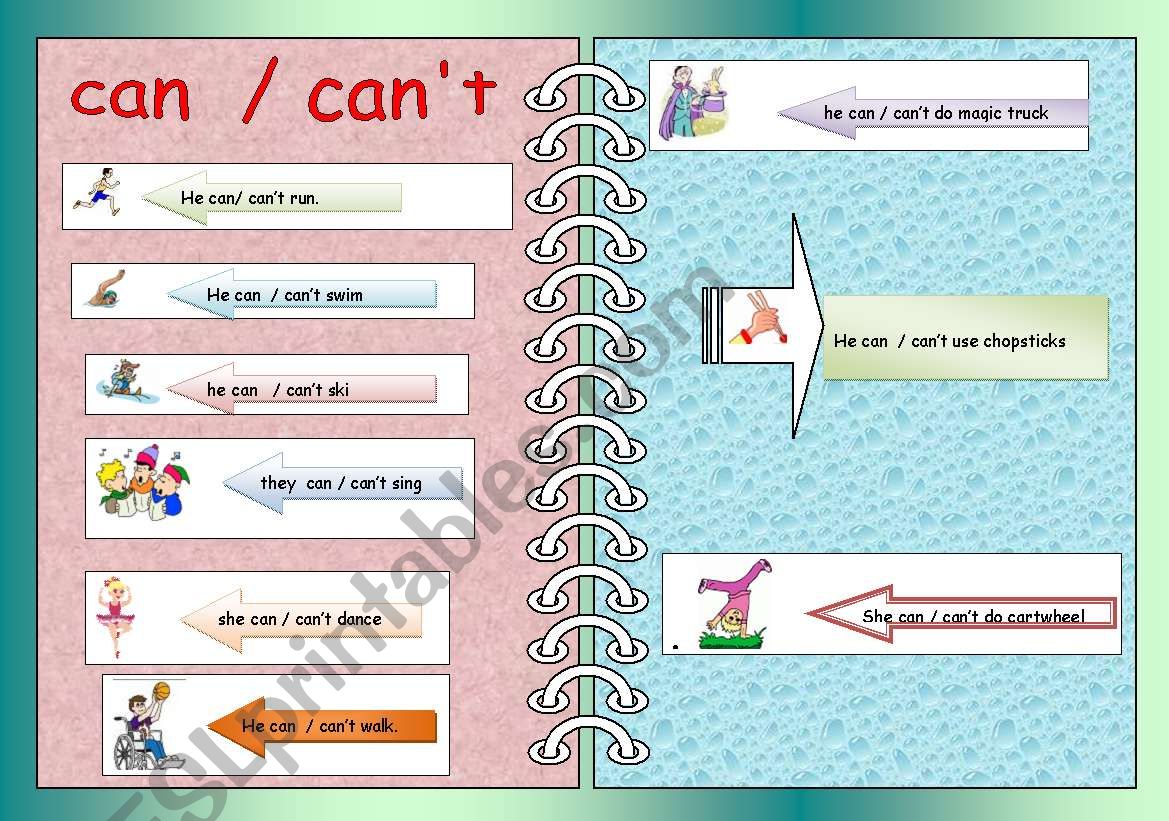
Can’t (Cannot): This is the most common and versatile modal for expressing present or future inability. It signifies a general lack of skill, opportunity, or permission.

- Examples: "I can’t swim." (lack of skill) / "She can’t come to the party tonight." (lack of opportunity/permission) / "You cannot park here." (lack of permission)
-

Couldn’t (Could not): This is the past tense form of "can’t." It denotes an inability that existed in the past, either generally or in a specific situation.
- Examples: "He couldn’t understand the lecture yesterday." (past inability in a specific situation) / "When I was younger, I couldn’t reach the top shelf." (general past inability)


-

Be unable to: This phrase is more formal and flexible than "can’t" or "couldn’t" because it can be used across all tenses (present, past, future, perfect, etc.) by conjugating the verb "to be." It emphasizes a lack of capacity or the state of not being able to do something.
- Examples: "I am unable to attend the meeting." (present formal) / "They were unable to finish the project on time." (past formal) / "We will be unable to process your request without more information." (future formal)

The subtleties between these forms, especially couldn't and didn't manage to, or the formality of be unable to versus the casual can't, often pose challenges for learners. This is precisely where targeted practice, facilitated by well-structured modals of inability worksheets, becomes crucial.
The Pedagogical Powerhouse: Why Worksheets Are Essential
Worksheets are not merely busywork; they are powerful pedagogical tools that facilitate active learning, reinforce grammatical structures, and provide immediate opportunities for application. For modals of inability, their importance cannot be overstated for several reasons:
- Active Engagement: Unlike passive listening or reading, worksheets require learners to actively recall, analyze, and apply grammatical rules. This hands-on approach promotes deeper understanding and retention.
- Reinforcement and Repetition: Mastery of grammar often comes through repeated, meaningful exposure. Worksheets provide structured opportunities for learners to practice using "can’t," "couldn’t," and "be unable to" in various contexts, embedding the patterns in their minds.
- Immediate Application: Learners can directly apply the rules they’ve just learned, allowing them to test their understanding and make mistakes in a low-stakes environment.
- Diagnostic Tool: For educators, completed worksheets serve as a valuable diagnostic tool. They quickly reveal common errors, areas of confusion, and individual learning gaps, enabling teachers to provide targeted feedback and adjust future instruction.
- Confidence Building: Successfully completing exercises builds learners’ confidence in their ability to use the target language structures correctly, encouraging further exploration and communication.
Types of Effective Modals of Inability Worksheets Exercises
To maximize the effectiveness of modals of inability worksheets, a variety of exercise types should be employed. This keeps learners engaged, addresses different learning styles, and provides a holistic understanding of the target grammar.
-
Fill-in-the-Blanks:
- Description: Learners complete sentences by inserting the correct modal of inability (
can't,couldn't,be unable to) based on context. - Benefit: Excellent for initial recognition and basic application.
- Example: "I missed the bus, so I __ get to school on time yesterday." (couldn’t)
- Description: Learners complete sentences by inserting the correct modal of inability (
-
Sentence Transformation/Rephrasing:
- Description: Learners rewrite sentences, changing the modal or phrase expressing inability without altering the meaning. For instance, transforming a sentence with "can’t" into one using "be unable to."
- Benefit: Encourages understanding of semantic equivalents and formal vs. informal usage.
- Example: "She can’t speak French very well." → "She __ speak French very well." (is unable to)
-
Error Correction:
- Description: Learners identify and correct grammatical errors in sentences where modals of inability are used incorrectly.
- Benefit: Develops critical thinking skills and helps learners recognize common mistakes.
- Example: "I didn’t can finish the race." → "I couldn’t finish the race."
-
Dialogue Completion:
- Description: Learners complete conversational exchanges using appropriate modals of inability, based on the preceding lines.
- Benefit: Simulates real-life communication, fostering an understanding of modals in context.
- Example:
- A: "Can you help me with this heavy box?"
- B: "I’m sorry, I ___. My back hurts." (can’t)
-
Situation-Based Sentence Creation:
- Description: Learners are given a scenario or a picture and asked to create sentences expressing inability related to it.
- Benefit: Encourages creative application and connects grammar to real-world situations.
- Example: Picture of a person trying to lift a huge rock. "He __ lift the rock because it’s too heavy." (can’t/is unable to)
-
Multiple Choice Questions:
- Description: Learners select the correct modal of inability from a given set of options.
- Benefit: Quick assessment of understanding, useful for quizzes or warm-up activities.
- Example: "After the accident, she (a) can’t (b) couldn’t (c) isn’t able to walk for several weeks." (b)
-
Matching Exercises:
- Description: Learners match situations or problems with appropriate statements of inability.
- Benefit: Reinforces cause-and-effect relationships and contextual understanding.
- Example: Match: "The power went out." with "I couldn’t finish my work on the computer."
-
Creative Writing Prompts:
- Description: Learners write a short paragraph, story, or diary entry incorporating several instances of modals of inability.
- Benefit: Promotes extended writing practice and integrated use of grammar.
- Example: "Write about a day when everything went wrong, using ‘can’t’ and ‘couldn’t’ at least five times."
Designing and Implementing Stellar Modals of Inability Worksheets
The quality of a worksheet significantly impacts its effectiveness. Here are key considerations for designing and implementing them:
- Clear Instructions: Ensure instructions are concise, unambiguous, and easy to understand, possibly with an example provided.
- Contextual Relevance: Integrate sentences and scenarios that are relatable and meaningful to learners. Abstract sentences provide less learning value.
- Progressive Difficulty: Start with simpler exercises (e.g., fill-in-the-blanks) and gradually move to more complex ones (e.g., error correction, creative writing). This scaffolding supports learners’ progression.
- Variety of Exercise Types: As discussed, mixing exercise formats keeps learners engaged and caters to different learning preferences.
- Answer Keys: Providing an answer key allows for self-correction and independent learning, empowering students to take responsibility for their progress.
- Visual Appeal: Use clear fonts, adequate spacing, and relevant images or graphics to make the worksheet inviting and less daunting.
- Differentiation: Create versions of the worksheet with varying levels of difficulty to cater to mixed-ability classes. Some students might need more scaffolding, while others are ready for more challenging tasks.
- Integration into Lesson Plans: Worksheets should not be standalone activities. Use them as warm-ups, main activity components, homework assignments, or review tools to reinforce specific lesson objectives.
Benefits for Learners and Educators
The advantages of well-crafted modals of inability worksheets extend to both sides of the classroom:
For Learners:
- Enhanced Accuracy: Consistent practice reduces errors in usage.
- Increased Fluency: Confident application of grammar leads to smoother communication.
- Self-Paced Learning: Learners can work at their own speed, reviewing difficult concepts as needed.
- Independent Practice: Fosters autonomy and responsibility for their own learning journey.
For Educators:
- Efficient Assessment: Quickly gauge student understanding and identify areas needing more attention.
- Targeted Instruction: Use worksheet results to inform future lesson planning and provide individualized support.
- Time-Saving: Ready-made or customizable worksheets save preparation time.
- Flexibility: Can be used for in-class activities, homework, remedial work, or extra practice for advanced students.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Even the best tools can be misused. Here are common pitfalls associated with modals of inability worksheets and how to overcome them:
- Over-reliance on One Type: Using only fill-in-the-blanks can become monotonous and may not foster deeper understanding. Solution: Diversify exercise types.
- Lack of Context: Sentences that are too abstract or out of context make it difficult for learners to grasp the nuances of usage. Solution: Use realistic, contextualized examples and scenarios.
- No Feedback Loop: Worksheets are less effective if students don’t receive feedback (either from an answer key or the teacher) on their performance. Solution: Always provide answer keys or dedicate time for review and correction.
- Difficulty Mismatch: Worksheets that are too easy or too difficult can demotivate learners. Solution: Assess student levels and differentiate accordingly.
The Digital Age and Modals of Inability Worksheets
In today’s technologically advanced world, modals of inability worksheets are no longer confined to paper. Many online platforms offer interactive exercises, digital fill-in-the-blanks, drag-and-drop activities, and even AI-powered feedback. Websites like ESL-Lounge, British Council LearnEnglish, and various educational apps provide a wealth of printable and interactive resources. These digital formats often come with immediate feedback, progress tracking, and gamified elements, further enhancing the learning experience. While digital resources are fantastic, the value of traditional printables for focused, distraction-free practice remains high.
Conclusion
The ability to express inability is a fundamental aspect of effective communication in English. Whether stating a personal limitation, describing a past challenge, or formally declining an invitation, the correct use of modals like "can’t," "couldn’t," and "be unable to" is paramount. For language learners striving for accuracy and fluency, modals of inability worksheets are not just supplementary materials; they are foundational components of a robust grammar curriculum.
By providing varied, contextualized, and progressively challenging exercises, these worksheets empower learners to actively engage with the language, reinforce grammatical structures through repetition, and build the confidence necessary to communicate their limitations clearly and correctly. For educators, they serve as invaluable tools for assessment, differentiation, and efficient lesson delivery. In essence, embracing the strategic use of well-designed modals of inability worksheets is a surefire way to unlock deeper understanding and pave the path to true communicative mastery for English language learners.
