
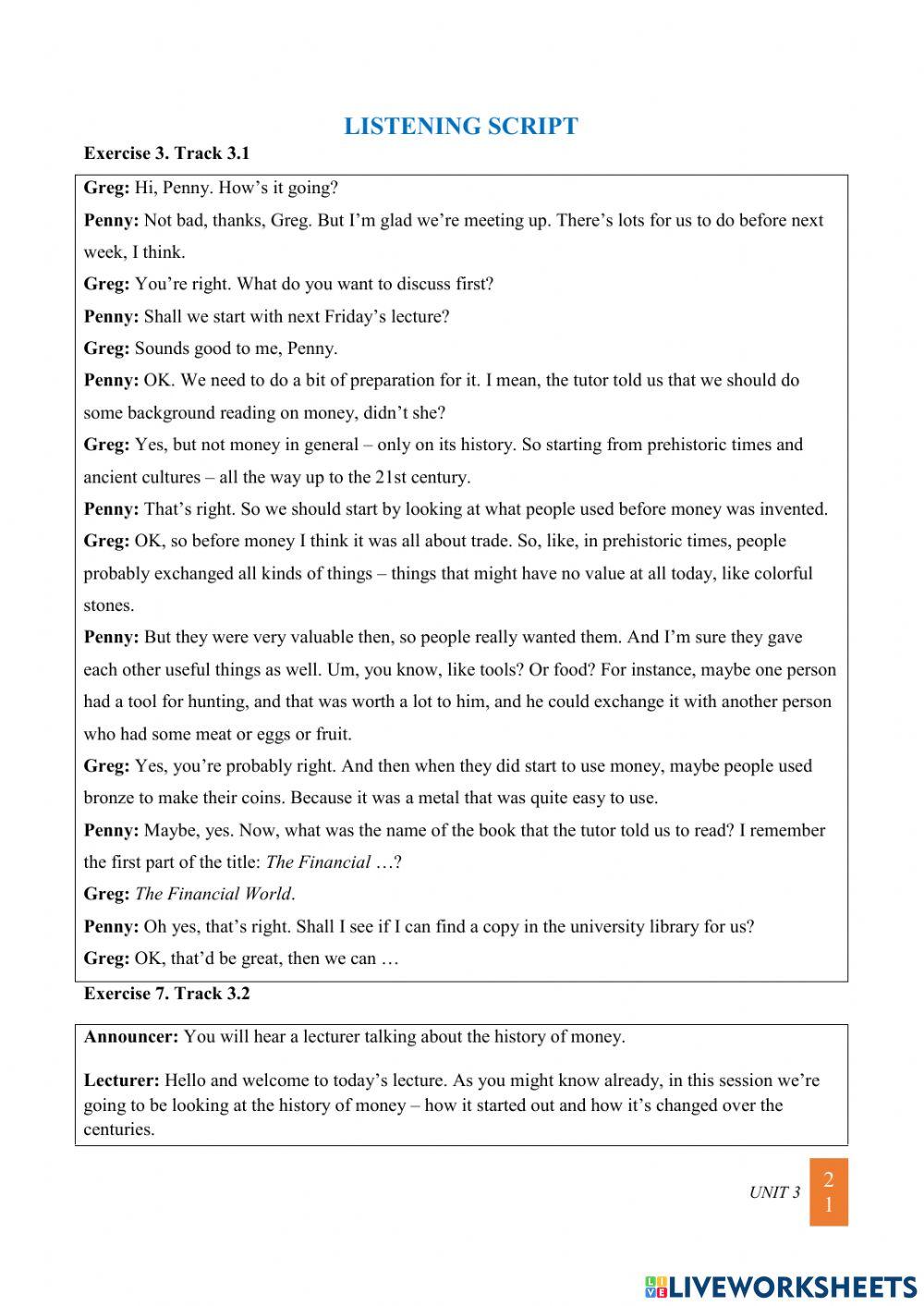
Mastering Aural Comprehension: The Power of Listening Scripts for ESL Worksheets
In the journey of second language acquisition, listening comprehension often presents one of the most formidable challenges. Unlike reading, where learners can control the pace and revisit text, spoken language is fleeting, often fast-paced, and laden with nuances like accents, intonation, and colloquialisms. For English as a Second Language (ESL) learners, developing robust listening skills is not merely about understanding words; it’s about grasping context, inferring meaning, and eventually, participating in real-time communication. This is where listening scripts for ESL worksheets emerge as an indispensable tool, acting as a crucial bridge between the ephemeral nature of spoken language and the concrete support learners need to decode, understand, and internalize what they hear.
This comprehensive article will delve into the profound importance of listening scripts, explore their various types, guide educators on crafting effective ones, and provide strategies for integrating them into engaging ESL worksheets to foster truly effective aural comprehension.
The Indispensable Role of Listening Scripts in ESL Instruction
Listening is often cited as the most difficult macro-skill for language learners to master. The reasons are multifaceted:

- Speed of Delivery: Native speakers often speak at a pace that overwhelms non-native listeners.
- Pronunciation and Accent Variation: Diverse accents and non-standard pronunciations can make even familiar words unintelligible.
- Connected Speech: Words often blend together (e.g., "gonna," "wanna"), making segmentation difficult.
- Vocabulary and Idioms: Unfamiliar words or idiomatic expressions can impede comprehension.
- Lack of Visual Cues: Unlike face-to-face conversations, many listening exercises lack the visual support of body language or facial expressions.



This is precisely where listening scripts for ESL worksheets prove their worth. A script, or transcript, provides a written version of the audio material, offering learners a tangible reference point. This allows them to:

- Verify Comprehension: Learners can listen first, then check their understanding against the script, identifying exactly where they struggled.
- Identify Unfamiliar Vocabulary: New words or phrases that were missed during listening become apparent in the written form, enabling targeted vocabulary acquisition.
- Analyze Pronunciation and Intonation: By seeing the words written while hearing them spoken, learners can connect sounds to spellings, notice stress patterns, and discern intonation, improving both their listening and speaking skills.
- Observe Grammar in Context: Scripts provide authentic examples of grammatical structures used naturally in conversation or monologue.
- Bridge the Gap: They help learners transition from relying on written cues to processing auditory information independently, gradually building confidence and reducing anxiety associated with listening tasks.



In essence, listening scripts transform an ephemeral auditory experience into a concrete, analyzable text, making the learning process more transparent and effective.
Types of Listening Scripts and Their Applications
The versatility of listening scripts for ESL worksheets lies in the wide array of audio materials they can accompany. Each type serves different pedagogical purposes:
-
Dialogues:
- Purpose: Ideal for practicing everyday conversations, social interactions, role-playing, and understanding turn-taking.
- Examples: Ordering food at a restaurant, asking for directions, making plans with a friend, job interviews, customer service interactions.
- Script Utility: Helps learners follow who is speaking, identify conversational fillers, and understand natural pauses and interruptions.
-
Monologues/Lectures:
- Purpose: Excellent for developing comprehension of longer, more formal discourse, extracting main ideas, identifying supporting details, and following logical arguments.
- Examples: Short news reports, weather forecasts, public announcements, academic mini-lectures, TED Talks (adapted for level).
- Script Utility: Allows learners to track complex information, identify topic sentences, and break down dense content into manageable chunks.
-
Narratives/Stories:
- Purpose: Enhances comprehension of chronological events, character development, and inferential skills. Great for engaging learners emotionally.
- Examples: Short fictional stories, personal anecdotes, historical accounts, biographies.
- Script Utility: Helps learners follow the plot, understand descriptive language, and identify sequence markers.
-
Instructions/Directions:
- Purpose: Crucial for practical application, ensuring learners can follow steps accurately.
- Examples: Recipes, assembly instructions, directions to a location, how-to guides.
- Script Utility: Essential for verifying step-by-step understanding and identifying specific vocabulary related to processes.
-
Authentic Materials:
- Purpose: Exposes learners to real-world language as it is naturally spoken, including hesitations, repetitions, and background noise (when appropriate).
- Examples: Snippets from podcasts, TV shows, movie clips, interviews with native speakers (adapted for level).
- Script Utility: While challenging, scripts for authentic materials are invaluable for advanced learners to grasp the nuances of natural, unscripted speech.
The choice of script type should always align with the learning objectives and the proficiency level of the ESL learners.
Crafting Effective Listening Scripts for ESL Worksheets
The quality of the script directly impacts its pedagogical value. Educators must consider several factors when creating or selecting listening scripts for ESL worksheets:
- Clarity and Simplicity (for lower levels): For beginners, scripts should use straightforward language, clear pronunciation, and a moderate pace. Avoid overly complex sentence structures or obscure vocabulary that isn’t the target of the lesson.
- Authenticity (for higher levels): As learners advance, introduce more authentic language, including common idioms, phrasal verbs, and even natural fillers (e.g., "um," "uh," "you know") to prepare them for real-world listening. However, this should be introduced gradually and purposefully.
- Purpose-Driven Content: Every script should have a clear learning objective. Is it for vocabulary acquisition, grammatical structure practice, identifying main ideas, or understanding specific details? The content and accompanying worksheet activities should reflect this purpose.
- Varying Difficulty: Provide a range of scripts that gradually increase in complexity. Start with shorter, simpler dialogues and progress to longer monologues or more nuanced conversations.
- Engaging and Relevant Topics: Learners are more motivated to listen to content that is interesting and relevant to their lives or academic pursuits. Topics such as travel, daily routines, popular culture, or current events often resonate well.
- High-Quality Audio Recording: Even the most perfectly crafted script is useless if the audio quality is poor. Ensure recordings are clear, free from excessive background noise, and spoken by native or near-native speakers with standard pronunciation.
- Accurate Transcription: The script must be an exact written representation of the audio. Any discrepancies can confuse learners and undermine the script’s utility. Include speaker labels (e.g., "Sarah:", "Mark:") for dialogues.
- Annotation (Optional but Recommended): For challenging sections, consider adding brief annotations to the script explaining difficult vocabulary, idiomatic expressions, or cultural references. This can be particularly helpful for self-study.
Designing Engaging Worksheets to Accompany Scripts
A script alone is not enough; it needs a well-designed worksheet to maximize its learning potential. Effective worksheets guide learners through a structured listening process:
-
Pre-Listening Activities:
- Purpose: Activate prior knowledge, introduce key vocabulary, predict content, and set a purpose for listening.
- Examples: Brainstorming related words, discussing the topic, looking at images, predicting what will happen based on the title.
-
While-Listening Activities:
- Purpose: Focus learners’ attention on specific aspects of the audio and provide immediate comprehension checks.
- Examples:
- Gap-filling: Learners fill in missing words or phrases from the script.
- True/False statements: Learners determine the accuracy of statements based on the audio.
- Multiple-choice questions: Learners select the best answer from given options.
- Specific information extraction: Learners listen for names, dates, numbers, or particular details.
- Ordering events: Learners sequence events as they occur in the audio.
- Note-taking templates: Learners fill in specific categories of information.
-
Post-Listening Activities:
- Purpose: Consolidate understanding, encourage critical thinking, and provide opportunities for speaking, writing, and further research.
- Examples:
- Discussion questions: Learners discuss the content of the audio.
- Summarization: Learners summarize the main points in their own words.
- Role-play: Learners act out the dialogue from the script or create their own based on the topic.
- Debate: Learners discuss opinions related to the audio content.
- Vocabulary review: Activities to reinforce new words learned from the script.
- Pronunciation practice: Learners read parts of the script aloud, focusing on intonation and rhythm.
Crucially, the worksheet should also include an answer key for self-correction, especially for self-study or homework assignments. The integration of listening scripts for ESL worksheets with these varied activities transforms a passive listening experience into an active, multi-faceted learning opportunity.
Best Practices for Integrating Scripts into ESL Instruction
To fully leverage the power of listening scripts, educators should employ specific pedagogical strategies:
-
Scaffolding the Listening Process: Don’t just hand over the script immediately.
- First Listen: No script, focus on main idea.
- Second Listen: No script, focus on specific details.
- Third Listen: With the script, for verification, detailed analysis, and pronunciation work.
- Subsequent Listens: Learners can listen and read simultaneously, or listen and shadow-read.
-
Contextualization is Key: Always provide background information or activate schema before listening. This prepares learners and makes the content more relatable.
-
Focus on Specific Skills: Use the script to zero in on particular listening sub-skills, such as identifying stress and intonation, recognizing reduced forms, or understanding idiomatic expressions.
-
Encourage Active Listening Strategies: Teach learners to predict, infer, listen for keywords, and identify the speaker’s purpose or tone. The script can then be used to confirm their hypotheses.
-
Promote Self-Correction and Autonomy: With the script and answer key, learners can independently identify their errors and understand why they made them. This fosters greater learner autonomy and responsibility for their own learning.
-
Integrate Technology: Utilize language labs, online platforms, or apps where learners can control the playback speed, loop sections, and access the script alongside the audio. Many platforms allow for interactive gap-fills directly on the screen.
Challenges and Solutions
While listening scripts for ESL worksheets are invaluable, their implementation can present challenges:
- Challenge: Finding or Creating Suitable Materials: High-quality, level-appropriate audio with accurate transcripts can be time-consuming to create or difficult to find.
- Solution: Utilize reputable ESL textbook series, online resources (e.g., Breaking News English, ESL-LAB), or adapt authentic materials by simplifying language and providing glossary. Collaborating with other teachers can also ease the burden.
- Challenge: Over-Reliance on the Script: Learners might be tempted to just read the script without truly listening.
- Solution: Emphasize the multi-stage listening process. Start with no script, then introduce it. Design activities that require listening first (e.g., "What did the speaker say before this phrase?").
- Challenge: Technical Issues: Poor audio quality or inaccessible technology can hinder learning.
- Solution: Invest in good recording equipment if creating your own. Ensure reliable internet access and devices for playback. Have backup plans (e.g., pre-downloading audio).
Conclusion
In the dynamic landscape of ESL education, listening scripts for ESL worksheets stand out as a fundamental and highly effective resource. They demystify the complexities of spoken English, providing learners with a tangible anchor in the often-overwhelming sea of auditory input. By offering a visual representation of what is heard, these scripts empower learners to dissect language, understand nuances, and build confidence in their comprehension abilities.
From the careful crafting of authentic yet accessible scripts to the thoughtful design of pre-, while-, and post-listening activities, educators play a pivotal role in harnessing the full potential of these tools. When integrated strategically, listening scripts for ESL worksheets don’t just facilitate understanding; they transform the listening experience from a passive reception of sound into an active, analytical, and ultimately, empowering journey towards true aural proficiency in English. For any ESL curriculum aiming to foster well-rounded language learners, the diligent use of listening scripts is not merely an option, but a necessity.
