
Mastering Degrees of Comparison: A Comprehensive Guide to Comparative vs. Superlative Worksheets
In the intricate world of English grammar, mastering the degrees of comparison is a cornerstone for clear and precise communication. Adjectives and adverbs transform to indicate varying levels of quality, quantity, or manner, allowing us to compare two items or highlight one among many. For language learners and educators alike, the effective acquisition of these grammatical structures often hinges on targeted practice, making a well-designed comparative vs superlative worksheet an invaluable tool. This article will delve deep into the pedagogical significance, diverse formats, and best practices for utilizing and creating worksheets that effectively teach and reinforce comparative and superlative forms, aiming for a comprehensive understanding that spans over 1200 words.
The Foundation: Understanding Comparative and Superlative Forms
Before diving into worksheets, it’s essential to solidify the core concepts:
1. Comparative Forms:

Comparative forms are used when comparing two nouns, pronouns, or actions. They indicate that one item possesses a quality to a greater or lesser degree than another.

- Formation for Adjectives:

- Short adjectives (1-2 syllables): Add "-er" to the end (e.g., tall → taller, fast → faster, happy → happier – note the ‘y’ to ‘i’ change).
- Longer adjectives (3+ syllables): Use "more" or "less" before the adjective (e.g., beautiful → more beautiful, difficult → more difficult, expensive → less expensive).
- Irregular adjectives: Some adjectives have unique comparative forms (e.g., good → better, bad → worse, far → farther/further).
- Formation for Adverbs:
- Short adverbs: Add "-er" (e.g., fast → faster, soon → sooner).
- Adverbs ending in -ly: Use "more" or "less" (e.g., quickly → more quickly, carefully → more carefully).
- Irregular adverbs: (e.g., well → better, badly → worse).


- Key Phrase: Often followed by "than" (e.g., "She is taller than her brother.").



2. Superlative Forms:
Superlative forms are used when comparing three or more nouns, pronouns, or actions, or when highlighting one item as possessing a quality to the highest or lowest degree within a group.
- Formation for Adjectives:
- Short adjectives (1-2 syllables): Add "-est" to the end (e.g., tall → tallest, fast → fastest, happy → happiest).
- Longer adjectives (3+ syllables): Use "most" or "least" before the adjective (e.g., beautiful → most beautiful, difficult → most difficult, expensive → least expensive).
- Irregular adjectives: (e.g., good → best, bad → worst, far → farthest/furthest).
- Formation for Adverbs:
- Short adverbs: Add "-est" (e.g., fast → fastest, soon → soonest).
- Adverbs ending in -ly: Use "most" or "least" (e.g., quickly → most quickly, carefully → most carefully).
- Irregular adverbs: (e.g., well → best, badly → worst).
- Key Phrase: Almost always preceded by "the" (e.g., "He is the tallest in his class.").
The subtle yet significant distinctions between comparative and superlative forms are precisely why focused practice through a comparative vs superlative worksheet is so crucial.
The Pedagogical Value of a Comparative vs. Superlative Worksheet
The utility of a well-designed comparative vs superlative worksheet cannot be overstated in language education. They serve multiple vital functions:
- Reinforcement and Practice: Grammar rules, no matter how clearly explained, require repetition and active application to be internalized. Worksheets provide a structured environment for this essential practice.
- Error Identification and Correction: By completing exercises, students encounter situations where they might make mistakes. This allows educators to identify common pitfalls and provide targeted feedback, preventing the fossilization of errors.
- Active Learning: Unlike passive listening or reading, completing a worksheet requires active engagement with the material, leading to deeper processing and retention.
- Assessment Tool: Worksheets can serve as informal or formal assessments, allowing teachers to gauge student understanding and progress before moving on to new concepts.
- Differentiation: Worksheets can be easily adapted to suit different learning levels, offering simpler exercises for beginners and more complex challenges for advanced learners.
- Independent Study: For self-learners or students needing extra practice, worksheets offer a clear path for independent study and self-assessment (especially with an answer key).
- Focus on Specific Rules: A worksheet can specifically target the irregular forms, the ‘y’ to ‘i’ change, or the correct use of "more/most" vs. "-er/-est," isolating challenging aspects for focused attention.
Diverse Formats of Comparative vs. Superlative Worksheets
A truly effective comparative vs superlative worksheet incorporates a variety of exercise types to maintain student engagement and address different learning styles.
-
Fill-in-the-Blanks:
- Basic: Provide a sentence with a blank and a base adjective/adverb in parentheses.
- Example: "My dog is (big) __ than your cat." (bigger)
- Advanced: Provide two blanks, one for the degree of comparison and one for "than/the."
- Example: "Sarah is (intelligent) __ __ student in the class." (the most intelligent)
- Basic: Provide a sentence with a blank and a base adjective/adverb in parentheses.
-
Sentence Transformation:
- Students rewrite sentences using comparative or superlative forms.
- Example: "The red car is fast. The blue car is faster. The green car is the fastest." (Combine into one sentence using degrees of comparison.)
- Example: "The book is interesting. (Comparative)" → "The book is more interesting than the movie."
- Students rewrite sentences using comparative or superlative forms.
-
Error Correction:
- Present sentences with grammatical errors related to comparatives/superlatives.
- Example: "She is more taller than him." → "She is taller than him."
- Example: "This is the most best day ever." → "This is the best day ever."
- Present sentences with grammatical errors related to comparatives/superlatives.
-
Multiple Choice:
- Students choose the correct comparative or superlative form from given options.
- Example: "Mount Everest is __ mountain in the world. (tall / taller / the tallest)"
- Students choose the correct comparative or superlative form from given options.
-
Matching Exercises:
- Match base adjectives/adverbs with their correct comparative and superlative forms, especially useful for irregular forms.
-
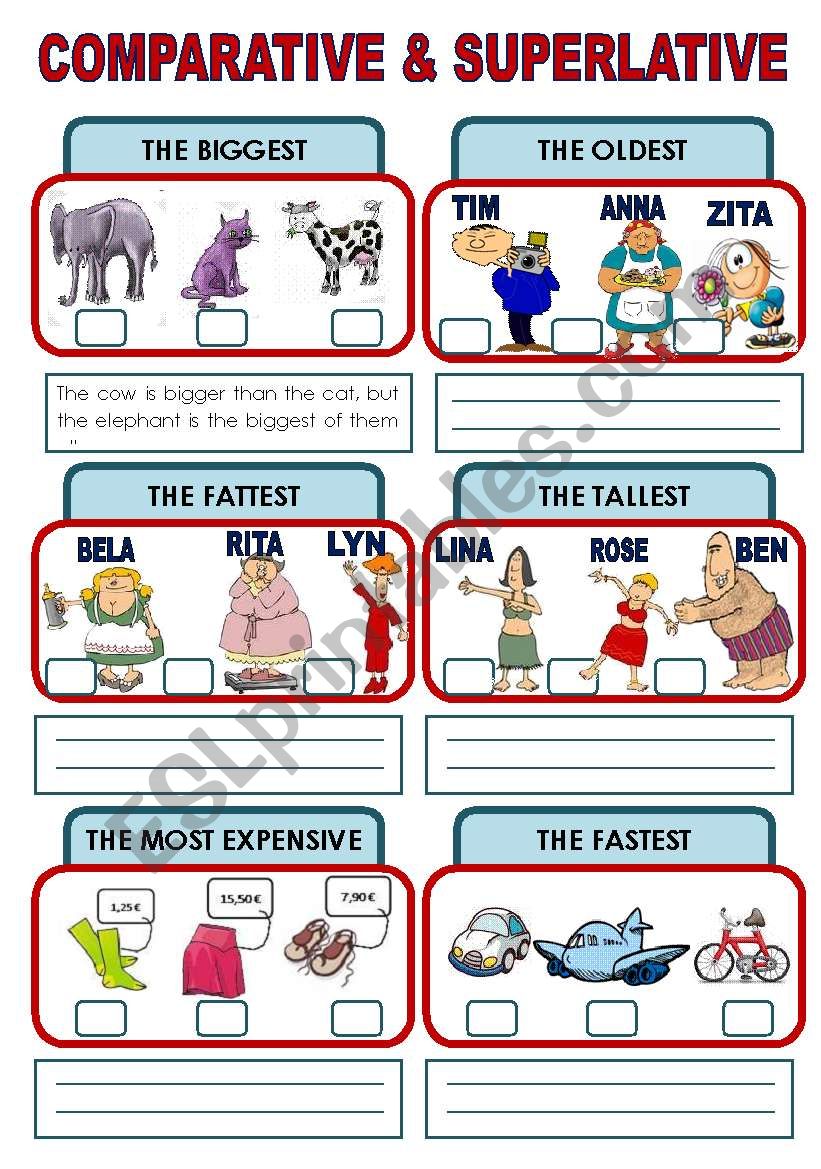
Picture-Based Activities:
- Show images of objects or people and ask students to write sentences comparing them.
- Example: Three pictures (a small dog, a medium dog, a large dog). Students write: "The medium dog is bigger than the small dog. The large dog is the biggest."
- Show images of objects or people and ask students to write sentences comparing them.
-
Dialogue/Paragraph Completion:
- Provide a short conversation or paragraph with blanks where students insert appropriate comparative or superlative forms based on context. This helps develop contextual understanding.
-
Real-World Application Scenarios:
- Ask students to compare products (e.g., phones, cars), travel destinations, or even historical figures using comparative and superlative forms. This makes the grammar relevant and engaging.
Designing an Effective Comparative vs. Superlative Worksheet
When creating a highly effective comparative vs superlative worksheet, several key principles should be considered to maximize its pedagogical impact:
- Clear and Concise Instructions: Students should immediately understand what is expected of them. Use simple language and provide an example if necessary.
- Gradual Difficulty (Scaffolding): Start with simpler exercises (e.g., fill-in-the-blanks with regular adjectives) and progressively introduce more complex ones (e.g., irregular forms, adverbs, longer sentences, contextual paragraphs).
- Contextual Relevance: Sentences should make sense and ideally relate to topics that are interesting or familiar to the students. Abstract, disconnected sentences can be demotivating.
- Variety of Exercise Types: As discussed above, mixing formats keeps students engaged and caters to different learning preferences.
- Focus on Common Pitfalls: Design exercises that specifically target common errors, such as:
- Overuse of "more/most" with short adjectives (e.g., "more bigger").
- Omitting "the" before superlatives.
- Confusing "than" and "then."
- Incorrectly forming irregular adjectives/adverbs.
- Inclusion of Irregular Forms: Dedicate a significant portion of the worksheet to irregular forms (good/better/best, bad/worse/worst, etc.), as these are often challenging.
- Clear Layout and Visual Appeal: A well-organized worksheet with sufficient white space is less intimidating and easier to navigate. Use clear fonts and consider incorporating relevant images.
- Answer Key: Providing an answer key allows students to self-check their work, promoting independent learning and immediate feedback. For educators, it streamlines grading.
- Differentiation Options: Create slightly easier and harder versions of the same worksheet. For instance, the easier version might provide word banks, while the harder one requires students to generate forms independently.
Common Pitfalls and How Worksheets Can Address Them
Students frequently make specific errors when dealing with degrees of comparison. A well-designed comparative vs superlative worksheet can specifically target and remedy these issues:
- Double Comparisons: Students might say "more better" or "most fastest." Worksheets can include sentences like "He is more taller than his sister" and ask students to correct them, explicitly explaining why only one form of comparison is needed.
- Misuse of "Than" and "The": Errors like "She is taller then me" or "He is tallest in the class" are common. Exercises focusing on sentence completion, where students must choose between "than" or "the," can reinforce correct usage.
- Confusion Between Comparative and Superlative: Students might use a superlative when a comparative is needed, or vice-versa. Contextual exercises where students must analyze the number of items being compared are effective.
- Incorrect Formation of Irregular Forms: "Goodest" or "badder" are frequent mistakes. Matching, fill-in-the-blank, and error correction exercises specifically for irregular forms are crucial.
- Adjective vs. Adverb Confusion: While often similar in form, ensuring students use the correct degree for adjectives modifying nouns and adverbs modifying verbs is important. Worksheets can present sentences where students choose between adjective and adverb forms.
Integrating Worksheets into a Broader Curriculum
A comparative vs superlative worksheet should not be an isolated activity. It functions best when integrated into a broader lesson plan:
- Pre-Lesson Diagnostic: Use a short worksheet to gauge students’ existing knowledge before introducing the topic.
- In-Class Practice: After explaining the rules, students can immediately apply them with a worksheet, allowing the teacher to circulate and provide immediate support.
- Homework: Assign worksheets for independent practice to consolidate learning outside the classroom.
- Review and Reinforcement: Use worksheets as review material before tests or as warm-up activities in subsequent lessons.
- Project-Based Learning: Incorporate comparative and superlative forms into larger projects, such as comparing two countries, writing a product review, or debating which historical figure was "the most influential."
Finding and Utilizing Resources for Comparative vs. Superlative Worksheets
For educators and learners, a wealth of resources exists for finding or creating an excellent comparative vs superlative worksheet:
- Online ESL/Grammar Websites: Many reputable sites (e.g., British Council LearnEnglish, ESL-Lounge, EnglishClub) offer free printable worksheets covering various grammar topics, often with answer keys.
- Teachers Pay Teachers (TpT): This platform hosts thousands of educator-created resources, including paid and free worksheets, often with creative designs and varied exercise types.
- Textbooks and Workbooks: Traditional English language learning textbooks typically include dedicated sections and exercises on comparative and superlative forms.
- Grammar Apps and Online Quizzes: Interactive platforms can provide immediate feedback, making learning more engaging. While not traditional worksheets, they serve a similar purpose.
- Creating Your Own: Tailoring worksheets to specific student needs or current curriculum topics can be highly effective. This allows for personalized examples relevant to the students’ lives or interests.
When utilizing external resources, always preview the comparative vs superlative worksheet to ensure its accuracy, clarity, and suitability for your learners’ level. Customization – even minor tweaks – can significantly enhance its effectiveness.
Conclusion
The ability to accurately use comparative and superlative forms is a hallmark of proficient English communication. It allows speakers and writers to express nuances of degree, making their language more precise, vivid, and impactful. The strategic use of comparative vs superlative worksheets is a cornerstone of effective language education, providing the structured, repetitive, and varied practice necessary for students to move from understanding the rules to confidently applying them in real-world contexts. By embracing diverse formats, focusing on common pitfalls, and integrating worksheets thoughtfully into the curriculum, educators can empower their students to master these essential grammatical structures, paving the way for greater fluency and communicative competence.
