
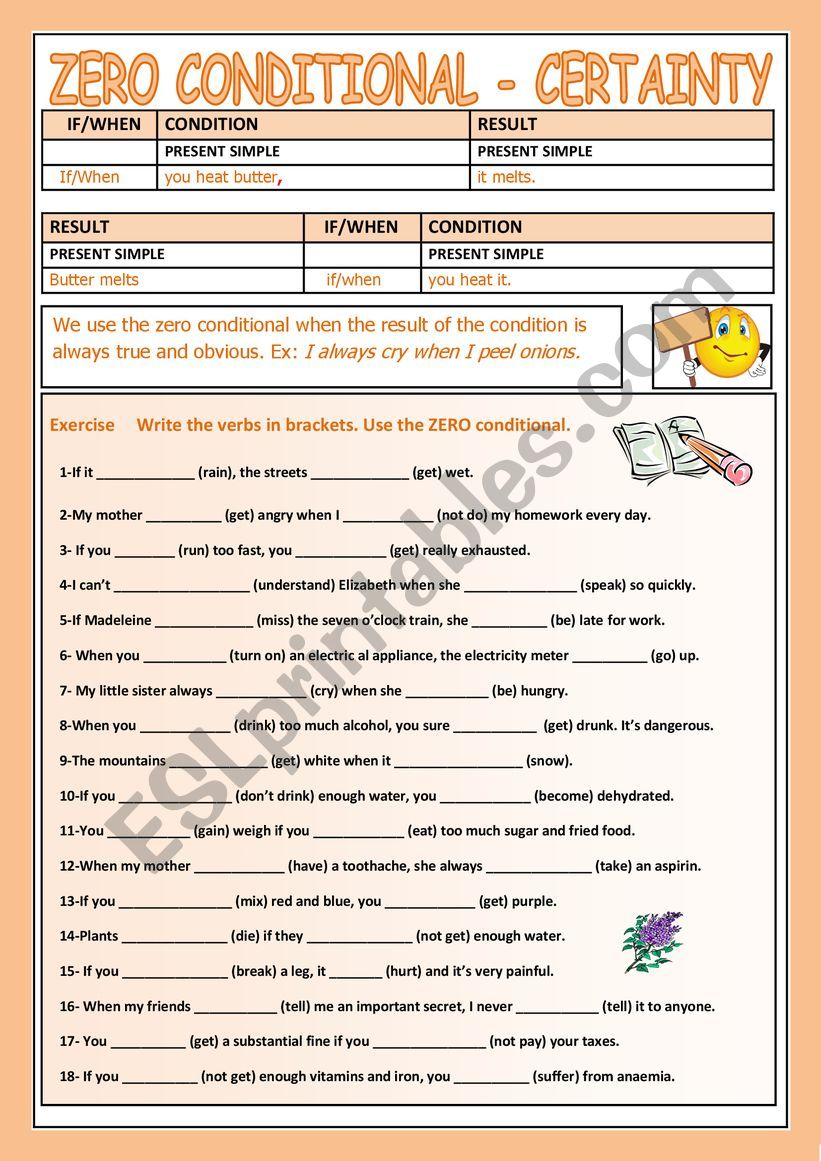
Mastering the Basics: The Indispensable Role of Zero Conditional Worksheets in Language Acquisition
In the intricate journey of mastering a new language, understanding grammatical structures is paramount. Among the foundational elements, the conditional sentences stand out as crucial for expressing cause and effect, possibilities, and general truths. Within this category, the zero conditional holds a unique and essential place, serving as the bedrock for understanding universal facts and predictable outcomes. For educators and self-learners alike, the effective acquisition of this grammatical concept often hinges on the strategic use of well-designed zero conditional worksheets. These invaluable tools provide the structured practice necessary to internalize the rule, apply it correctly, and build a robust understanding of its nuances.
Understanding the Zero Conditional: The Bedrock of Certainty
Before delving into the pedagogical utility of worksheets, it’s vital to solidify our understanding of the zero conditional itself. This grammatical structure is used to talk about general truths, scientific facts, habits, and situations where one event always leads to another. It expresses a certainty, a direct and unchanging cause-and-effect relationship.

The structure of the zero conditional is straightforward:

If + present simple, present simple.

Or, the clauses can be reversed:

Present simple if + present simple.

The "if" can often be replaced by "when" without changing the meaning, further emphasizing the certainty of the outcome.
Examples:
- If you heat water to 100 degrees Celsius, it boils. (Scientific fact)
- If I eat too much sugar, I feel sick. (General truth/habit)
- When it rains, the ground gets wet. (General truth)
- If you press that button, the machine turns on. (Instruction/predictable outcome)


The zero conditional is distinct from other conditionals (first, second, third) because it deals with situations that are always true, rather than possibilities, hypothetical situations, or past regrets. Its simplicity belies its importance, as it forms the basis for logical thought and clear communication about the world around us.

The Pedagogical Power of Zero Conditional Worksheets
Why are worksheets, specifically zero conditional worksheets, such an indispensable component of language learning? The answer lies in their ability to provide structured, repetitive, and varied practice that caters to different learning styles and reinforces grammatical concepts effectively.
-
Reinforcement and Repetition: Language acquisition, particularly grammar, thrives on repetition. Worksheets offer numerous opportunities to apply the zero conditional rule in various contexts, helping learners internalize the structure until it becomes second nature. This repetitive exposure solidifies memory pathways and automates correct usage.
-
Active Learning: Unlike passive listening or reading, completing a worksheet requires active engagement. Learners must recall the rule, analyze the context, and apply their knowledge, which deepens their understanding far more effectively than merely observing examples.
-
Identification of Gaps: Worksheets serve as diagnostic tools. As learners complete exercises, both they and their instructors can quickly identify areas of confusion or common errors. This allows for targeted intervention and clarification, addressing specific misunderstandings before they become ingrained.
-
Confidence Building: Successfully completing exercises on zero conditional worksheets provides learners with a sense of accomplishment. This positive reinforcement boosts their confidence, encouraging them to tackle more complex grammatical structures and use the language more freely.
-
Versatility and Flexibility: Worksheets can be used in diverse educational settings: in-class for guided practice, as homework for independent study, or for self-paced learning. They can be adapted for individual work, pair work, or small group activities, making them incredibly flexible tools for any curriculum.
Types of Effective Zero Conditional Worksheets
The effectiveness of zero conditional worksheets isn’t just in their existence but in their variety and design. A comprehensive set of materials will incorporate a range of exercise types to cater to different learning preferences and target various aspects of language proficiency.
-
Matching Exercises: These are excellent for beginners. Learners match the "if-clause" with its corresponding "result clause." For example, "If you mix blue and yellow…" could be matched with "…you get green." This helps learners grasp the direct cause-and-effect relationship.
-
Fill-in-the-Blanks: This classic exercise requires learners to conjugate verbs correctly in the simple present tense for both clauses. This directly targets the structural accuracy of the zero conditional.
- Example: If he (study) hard, he (pass) his exams. (Answers: studies, passes)
-
Sentence Completion: Similar to fill-in-the-blanks, but often more open-ended. Learners might be given an "if-clause" and asked to complete the "result clause" based on general knowledge or their own experiences, or vice versa. This encourages creative thinking within the grammatical framework.
- Example: If you heat ice, it ___.
-
Multiple Choice Questions: Useful for quick assessment and reinforcing correct forms. Learners choose the best option to complete a sentence or identify the grammatically correct zero conditional sentence among several choices.
-
Error Correction: This advanced exercise presents sentences with common errors (e.g., incorrect tense, missing commas, wrong vocabulary) and requires learners to identify and correct them. This promotes critical thinking and a deeper understanding of the rules.
- Example: If it will rain, the streets get wet. (Correction: If it rains, the streets get wet.)
-
Transformation Exercises: Learners might be asked to rewrite sentences from one form to another (e.g., from a declarative sentence to a zero conditional, or changing the order of the clauses). This hones their flexibility in manipulating the structure.
-
Picture-Based Activities: Visual learners benefit greatly from these. Learners observe a picture (e.g., a plant wilting) and describe the general truth using the zero conditional (e.g., If you don’t water plants, they die.). This connects grammar to real-world observations.
-
Dialogue and Role-Playing Prompts: While not strictly a "worksheet" in the traditional sense, prompts that encourage using the zero conditional in simulated conversations (e.g., giving instructions, describing habits, explaining scientific processes) transition learners from written practice to oral fluency.
-
True or False Statements: Learners read zero conditional statements and determine if they are generally true or false, providing a chance for discussion and reasoning.
- Example: If you drop a stone, it floats. (False)
Designing and Integrating Effective Worksheets
Creating or selecting effective zero conditional worksheets requires careful consideration of several factors:
- Clarity of Instructions: Instructions should be concise, unambiguous, and easy for learners to understand.
- Gradual Difficulty: Start with simpler exercises and progressively introduce more complex tasks. This scaffolding helps prevent overwhelm and builds confidence.
- Contextual Relevance: Use scenarios and topics that are relatable, interesting, and relevant to learners’ lives or general knowledge. This makes the grammar feel less abstract and more applicable.
- Variety: As discussed, incorporate a mix of exercise types to keep learners engaged and address different learning styles.
- Answer Keys: For self-study or quick checking, clear answer keys are essential.
- Opportunities for Discussion: Some exercises can serve as springboards for class discussions, encouraging learners to explain their answers or provide additional examples.
Integrating these worksheets into a lesson plan involves:
- Pre-teaching: Introduce the zero conditional concept with clear explanations and examples.
- Guided Practice: Use worksheets in class, working through exercises together, providing immediate feedback and clarification.
- Independent Practice: Assign worksheets as homework to reinforce learning and assess individual comprehension.
- Assessment: Use specific exercises to gauge mastery of the zero conditional.
- Review: Periodically revisit zero conditional concepts through quick worksheet drills to ensure long-term retention.
Common Challenges and How Worksheets Can Help
Learners often face specific challenges when acquiring the zero conditional:
-
Confusing with the First Conditional: The most common pitfall is mixing up the zero conditional (always true, certain) with the first conditional (possible future outcome). Worksheets that explicitly contrast these two or provide scenarios where only one is appropriate can clarify this distinction.
- Example: If you study, you pass (zero conditional – general truth about studying). VS. If you study, you will pass (first conditional – specific future possibility).
-
Verb Tense Errors: Learners might incorrectly use future tense or other tenses in one of the clauses. Fill-in-the-blank and error correction exercises specifically target the consistent use of the simple present tense.
-
Lack of Context: Without relevant scenarios, the grammar can feel abstract. Worksheets that use real-life examples, scientific facts, or common habits provide the necessary context.
-
Over-reliance on Translation: Some learners try to translate directly from their native language, which can lead to errors. Worksheets designed with clear English instructions and examples encourage thinking directly in English.
By thoughtfully addressing these challenges, zero conditional worksheets become powerful tools for guiding learners towards accurate and fluent use of this fundamental grammatical structure.
Conclusion
The zero conditional, with its straightforward structure and universal application, is a cornerstone of English grammar. Its mastery is not just about memorizing a rule but about understanding how to express unchanging truths, predictable outcomes, and logical cause-and-effect relationships. For language educators and learners alike, the journey to this mastery is significantly supported, if not accelerated, by the strategic implementation of high-quality zero conditional worksheets. From basic matching to complex error correction, these versatile resources offer the varied, active, and repetitive practice essential for internalizing the structure, building confidence, and ultimately, achieving a robust and accurate command of the English language. In an educational landscape increasingly focused on effective and engaging learning, the enduring value of well-crafted zero conditional worksheets remains undeniable.
