
Mastering the Building Blocks: The Essential Adjectives vs Nouns Worksheet
In the intricate tapestry of the English language, words are the threads that weave meaning, convey emotions, and paint vivid pictures. Among these threads, nouns and adjectives stand out as fundamental components, each playing a distinct yet often intertwined role. While seemingly straightforward, the distinction between these two parts of speech can sometimes blur, leading to confusion for learners of all levels. This is precisely where a well-designed adjectives vs nouns worksheet becomes an indispensable tool, offering clarity, practice, and a solid foundation for grammatical mastery.
This comprehensive article will delve into the nuances of nouns and adjectives, explore the common pitfalls that lead to their confusion, and elaborate on how an effective adjectives vs nouns worksheet can serve as the ultimate guide to understanding and applying these crucial linguistic elements.
The Foundation: Understanding Nouns
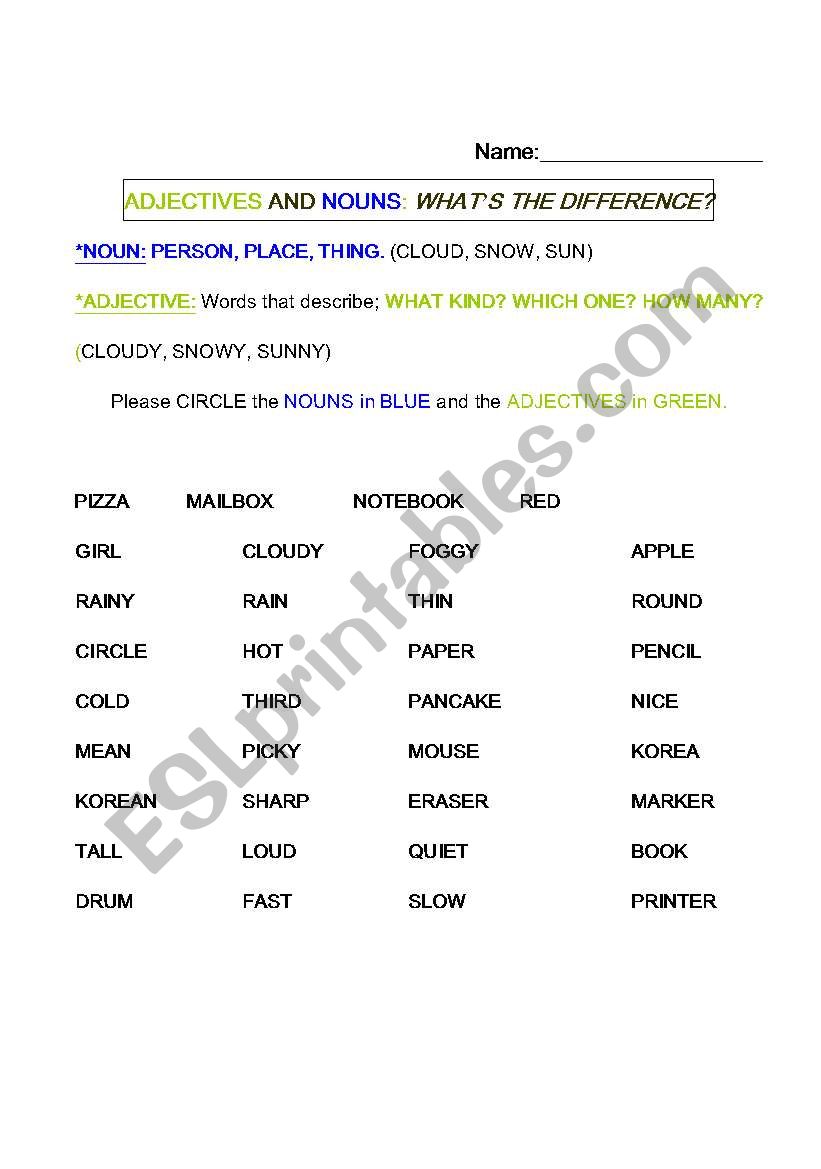
At its core, a noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. They are the labels we use to identify everything around us, from the tangible to the abstract.
Types of Nouns:
- Common Nouns: General names for people, places, things, or ideas (e.g., student, city, book, happiness).
- Proper Nouns: Specific names for people, places, or organizations, always capitalized (e.g., Sarah, London, Amazon).
- Concrete Nouns: Nouns that can be perceived by the five senses (e.g., table, dog, music, scent).
- Abstract Nouns: Nouns that represent ideas, qualities, or concepts that cannot be perceived by the senses (e.g., freedom, courage, love, justice).
- Collective Nouns: Nouns that refer to a group of people, animals, or things as a single unit (e.g., team, flock, committee, audience).

Function of Nouns:
Nouns primarily function as the subject of a sentence (who or what the sentence is about), the object of a verb (who or what receives the action), or the object of a preposition. They are the anchors of our sentences, providing the essential "what" or "who."

The Describers: Understanding Adjectives
If nouns are the anchors, then adjectives are the vibrant colors that bring those anchors to life. An adjective is a word that modifies or describes a noun or a pronoun. They provide additional information about the noun’s qualities, characteristics, quantity, or appearance.

Types of Adjectives:
- Descriptive Adjectives: These are the most common type, describing a quality of the noun (e.g., red car, tall building, intelligent student).
- Possessive Adjectives: Show ownership (e.g., my book, your house, their car). (Note: These are sometimes also classified as possessive pronouns, but they function as adjectives when modifying a noun).
- Demonstrative Adjectives: Point out specific nouns (e.g., this book, that car, these shoes, those ideas).
- Interrogative Adjectives: Used in questions to modify nouns (e.g., which way, whose car, what color).
- Indefinite Adjectives: Refer to non-specific nouns (e.g., few people, many books, some sugar, any problems).
- Articles: "a," "an," and "the" are also considered adjectives as they specify or generalize nouns (e.g., a dog, an apple, the sun).

Function of Adjectives:
Adjectives typically precede the noun they modify (e.g., "a beautiful flower") or follow a linking verb to describe the subject (e.g., "The flower is beautiful"). Their primary role is to add detail, specificity, and richness to the nouns they describe.
Why the Confusion? The Blurring Lines
Given their distinct definitions, why do learners often struggle with distinguishing between nouns and adjectives? Several factors contribute to this common confusion:
-
Words That Can Be Both: Some words can function as either a noun or an adjective depending on their context in a sentence.
- Example 1: "We need to install a new light." (Noun) vs. "The room was filled with light colors." (Adjective)
- Example 2: "She has a lot of guts." (Noun) vs. "He showed a guts feeling." (Adjective – though less common, or often hyphenated "gut-feeling")
- Example 3: "The elder arrived." (Noun) vs. "The elder statesman spoke." (Adjective)
-
Gerunds and Participles: These verb forms can sometimes function as nouns (gerunds) or adjectives (participles), further complicating identification.
- Gerund as Noun: "Running is good exercise." (The act of running)
- Present Participle as Adjective: "The running water soothed him." (Describes water)
- Past Participle as Adjective: "The broken vase lay on the floor." (Describes vase)
-
Compound Nouns and Adjective Phrases: When multiple words combine to form a single noun or an adjective phrase, it can be challenging to parse individual word functions.
- Compound Noun: "He works at the fire station." (Fire here modifies station, but together they form a noun concept).
- Adjective Phrase: "The man in the red hat is my uncle." (The entire phrase acts like an adjective describing "man").
-
Lack of Contextual Analysis: Students often try to identify words in isolation rather than analyzing their function within the sentence structure. The key to differentiation always lies in how the word is used.
The Power of an Effective Adjectives vs Nouns Worksheet
This is where the carefully crafted adjectives vs nouns worksheet proves its invaluable worth. It provides structured opportunities for learners to practice, reinforce, and ultimately internalize the distinctions. An ideal worksheet doesn’t just define; it challenges learners to apply their understanding in varied contexts.
Key Design Principles for an Effective Adjectives vs Nouns Worksheet:
- Clear Instructions: Ambiguous instructions lead to frustration. Each exercise should clearly state what the student needs to do.
- Gradual Difficulty: Start with simple identification tasks and progressively move towards more complex sentence analysis, transformation exercises, and contextual challenges.
- Varied Exercise Types: Repetition is good, but variety keeps engagement high.
- Real-World Examples: Sentences and scenarios that are relatable and meaningful to the learner enhance understanding and retention.
- Answer Key: Essential for self-assessment and for teachers to quickly review student work and provide targeted feedback.
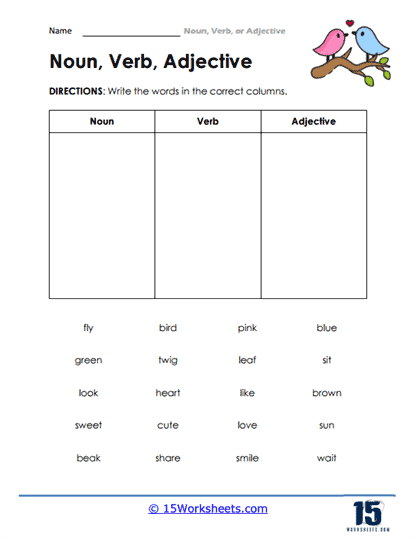
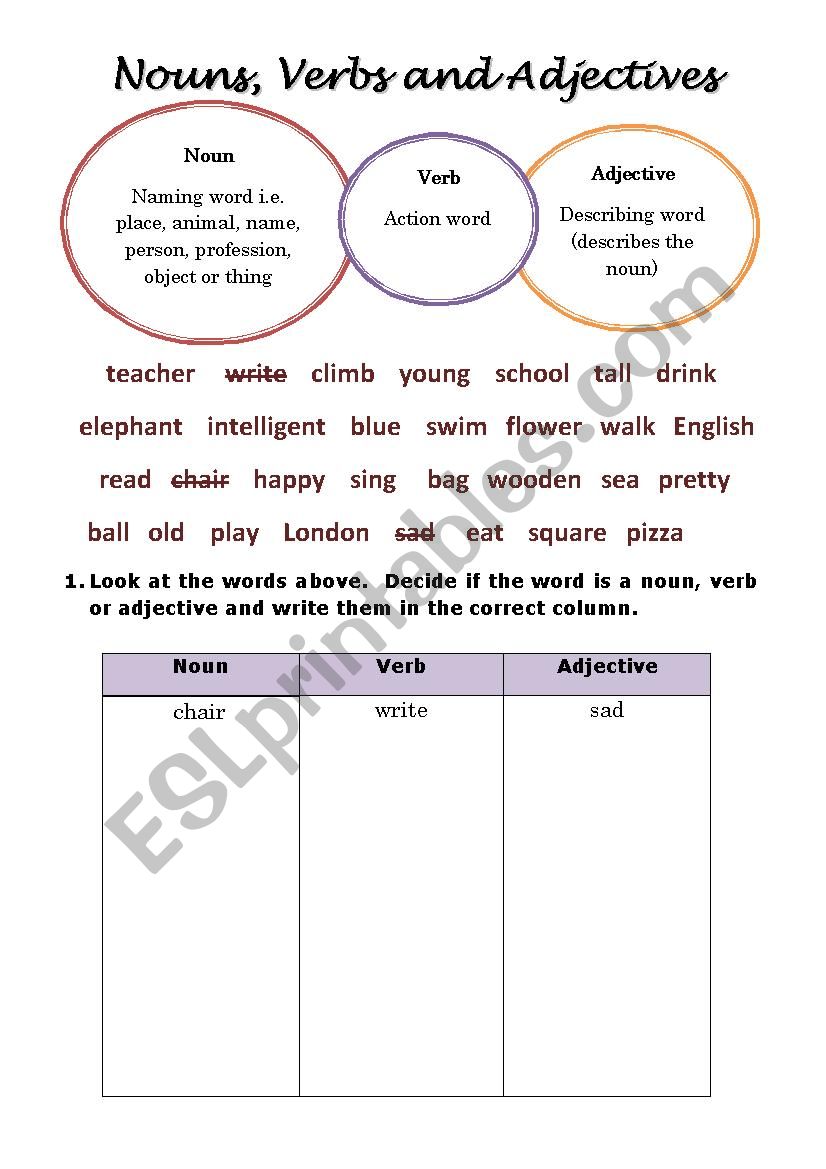
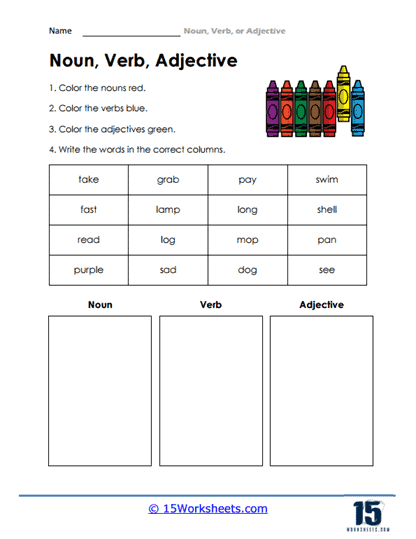
Types of Exercises to Include in an Adjectives vs Nouns Worksheet:
To truly solidify understanding, a comprehensive adjectives vs nouns worksheet should incorporate a range of exercise types:
-
Simple Identification:
- Task: Underline all the nouns and circle all the adjectives in the following sentences.
- Example: The big dog chased the small ball across the green field.
-
Categorization:
- Task: Read the words below and place them in the correct column (Noun or Adjective).
- Words: happy, book, brave, computer, intelligent, freedom, quiet, table, blue, courage.
-
Fill-in-the-Blanks (Choosing the Correct Part of Speech):
- Task: Complete the sentences with the correct word from the options provided, ensuring it fits as either a noun or an adjective.
- Example: The (bright/brightness) sun shone in the (sky/skylight).
- Example: Her (kind/kindness) was evident in her (gentle/gentleness) smile.
-
Sentence Creation:
- Task: Write two sentences for each word: one where it acts as a noun, and one where it acts as an adjective.
- Word: "fast"
- Noun: The car drove at a incredible fast. (Less common, but possible in specific contexts like "set a new fast")
- Adjective: The fast runner won the race.
- Word: "cold"
- Noun: The cold bit at his exposed skin.
- Adjective: She preferred cold weather.
-
Transformation Exercises:
- Task: Change the underlined noun into an adjective, or the underlined adjective into a noun, and rewrite the sentence.
- Example: The beauty of the sunset was breathtaking. (Noun to Adjective: The beautiful sunset was breathtaking.)
- Example: He was a very courageous person. (Adjective to Noun: He showed great courage.)
-
Contextual Analysis (Identifying Function):
- Task: Identify whether the underlined word is a noun or an adjective, and explain your reasoning based on its function in the sentence.
- Example: The sound of music filled the hall. (Noun, because it names what filled the hall.)
- Example: They played sound advice. (Adjective, because it describes the quality of the advice.)
Benefits of Consistent Practice with an Adjectives vs Nouns Worksheet
Regular engagement with a well-structured adjectives vs nouns worksheet yields numerous benefits for language learners:
- Reinforced Understanding: Repetitive exposure to examples and exercises solidifies the definitions and functions of each part of speech.
- Improved Sentence Construction: A clear grasp of nouns and adjectives helps learners build grammatically correct and descriptively rich sentences.
- Enhanced Reading Comprehension: Understanding how words function within a sentence improves the ability to decode meaning from complex texts.
- Critical Thinking Skills: Analyzing the role of each word in a sentence encourages critical thinking and attention to detail.
- Confidence Building: Success in identifying and using these fundamental parts of speech boosts a learner’s overall confidence in their language abilities.
Beyond the Basics: Tackling Nuances
While a good adjectives vs nouns worksheet will cover the primary distinctions, advanced learners can benefit from exercises that specifically target the tricky cases:
- Gerund vs. Participle: Differentiating between "Swimming is my favorite sport" (gerund/noun) and "The swimming pool is closed" (participle/adjective).
- Compound Nouns vs. Noun + Adjective: For instance, "football player" (compound noun) vs. "happy player" (adjective + noun). The former acts as a single naming unit.
- Nominalized Adjectives: Adjectives used as nouns to refer to a group (e.g., "the poor," "the rich").
Conclusion
The journey to grammatical proficiency is paved with understanding the fundamental building blocks of language. Nouns and adjectives, while distinct in their primary roles, can often pose a challenge due to their contextual flexibility and the existence of words that straddle both categories.
An expertly designed and consistently utilized adjectives vs nouns worksheet is not merely a collection of exercises; it is a vital pedagogical tool. It empowers learners to move beyond rote memorization, fostering a deep, functional understanding of how these essential parts of speech operate within the English language. By providing targeted practice, varied challenges, and opportunities for analytical thinking, a comprehensive adjectives vs nouns worksheet equips students with the precision and confidence needed to master the art of effective communication, one well-placed word at a time. Embrace the power of practice, and watch as the intricate world of English grammar becomes clearer and more accessible.
